
Gentians
are very variable in their morphology. Listed below are some traits that
occur in the family and their occurrence in some genera. Bibliographic
references are listed in parenthesis [ ] after the characters. More
information on most of these characters are available in Struwe et al.
(2002).
See
anatomy page for Anatomy, Palynology, Embryology, and Chemistry
characters.

Habit
(growth habit, trophy)
Roots,
hairs, stems
Leaves
(petioles, stipules)
Inflorescence
(branching, position, bracts)
Flowers
(see also Flower anatomy)
Calyx
(sepals; see also Flower anatomy)
Corolla
(petals; see also Flower anatomy)
Glands
in the flower (see also Flower anatomy)
Stamens
(androecium, filaments, anthers; see also Flower
anatomy)
Gynoecium
(pistil, ovary, style, stigma; see also Flower anatomy)
Fruits
(see also Flower anatomy)
Seeds
(see also Embryology)

Habit
(growth habit, trophy):
| |
trees:
e.g., Anthocleista, Chorisepalum, Fagraea,
Macrocarpaea,
Potalia, Prepusa, Symbolanthus
|
| |
shrubs:
e.g., Adenolisianthus,
Chorisepalum, Gentianothamnus,
Fagraea, Ixanthus, Macrocarpaea, Orphium, Potalia,
Prepusa, Saccifolium,
Symbolanthus,
Tachia
|
| |
woody
lianas
and climbers: e.g., Anthocleista spp., Lagenanthus, Purdieanthus
|
 |
herbaceous
climbers: e.g., Bisgoeppertia, Crawfurdia
|
| |
herbs:
most gentians
|
| |
single-stemmed
trees and shrubs (monocarpic): Potalia
|
| |
candelabra-shaped
branching: Anthocleista spp.
|
| |
leaves
crowded at branch apices: many in subtribe Potaliinae and tribe Helieae
|
| |
autotrophic
plants: most gentians
|
 |
heterotrophic
plants, mycotrophs, saprophytes: Bartonia (partly heterotrophic), Cotylanthera, Obolaria
(partly heterotrophic),
Sebaea oligantha, Voyria,
Voyriella
|
 |
dioecious
plants (male and female flowers on separate plants): Gentianella spp., Veratrilla.
All other gentians have flowers that have fully functional male (stamens)
and female (gynoecium) parts in the same flower.
|
| |
prostrate habit (horizontal branching on the ground, rooting at the nodes): Exacum spp.
|
Roots,
hairs, stems:
| |
taproots:
most gentians
|
| |
coralloid
roots, bird's nest roots (associated with mycorrhiza): Obolaria, Voyria,
Voyriella
|
| |
glabrous plants
(lacking hairs): most gentians
|
| |
hairy
plants:
Chironia
spp., Macrocarpaea spp., Microrphium, Ornichia, Orphium
|
| |
glandular
hairs:
|
 |
glaucous
plants (with a waxy, bluegreen surface layer): Blackstonia, Eustoma
|
| |
viscid
plants (sticky): Ixanthus
|
| |
bristles
on vegetative parts (hard, sharp hairs): Microrphium, Orphium
|
| |
corky
bark:
Saccifolium
|
| |
hollow
stems: common
|
| |
terete
(round) stems: common
|
| |
quadrangular
(4-cornered) stems: common
|
 |
winged
stems: common
|
Leaves
(petioles, stipules):
 |
opposite
leaves (leaves 2 and 2 along stem): nearly all gentians
|
| |
alternate
leaves (leaves single along stem):
Saccifolium,
Voyriella spp.
|
| |
whorled leaves (verticillate, 3 or more together along stem): Curtia spp., Exacum spp.
|
| |
leaves
in basal rosette (rosulate): many gentians, especially in Chironieae and Gentianeae,
e.g., Centaurium spp., Gentianella spp.
|
 |
amplexicaul/perfoliate
leaves (opposite leaves that are fused together at their bases): Exacum spp.,
Prepusa spp., Symphyllophyton, Tachiadenus spp.
|
| |
saccate
leaves (sack-shaped):
Saccifolium
|
| |
entire
leaves (margin smooth, not lobed or dissected): all gentians (except Irlbachia poeppigii and some
Fagraea)
|
| |
dentate
leaves (margin with teeth): Fagraea spp., Irlbachia poeppigii
|
| |
scale-like
leaves (leaves very small, like scales): Bartonia,
Cotylanthera, Sebaea
oligantha, Voyria, and
Voyriella
|
| |
interpetiolar
line (ridge between the base of a pair of leaves): most gentians
|
| |
interpetiolar
stipules (a flap of leaf-like tisse between a pair of leaves): Macrocarpaea spp.,
very rare in the family, only occurs in one species
|
| |
interpetiolar
sheath ( a ring of tissue around the stem at the base of a pair of leaves): Anthocleista, Chorisepalum, Fagraea, Lisianthius,
Macrocarpaea, Potalia
|
| |
auricules
at base of leaves (ear-shaped appendages at the base of a leaf): Anthocleista spp., Fagraea spp.
|
| |
axillary
spines (spines in the leaf axil): Anthocleista
|
 |
acrodromous
leaf venation (arcuate, few veins, bent towards apex of leaf): common
|
| |
brochidromous
leaf venation (pinnate, veins straight towards edge of leaf): common in some genera, e.g., Anthocleista,
Macrocarpaea spp.,
Fagraea,
|
Inflorescence
(branching, position, bracts):
 |
axillary
inflorescences (in leaf axils): many gentians, e.g.,
Enicostema,
Saccifolium, Tachia, Zonanthus
|
 |
terminal
inflorescences (at top of branch): many gentians
|
| |
solitary
flowers (flowers one by one, not together): Cotylanthera, Gentianothamnus,
Saccifolium
|
 |
cymes
(a type of inflorescence with a top flower and side branches that
repetitive branch sideways, symmetrically or assymmetrically):
most gentians
|
| |
racemes:
Fagraea spp.
|
| |
capitate
(flowers in tight heads): Cracosna, Tapeinostemon spp.
|
 |
spicate
(flowers in a spike):
Coutoubea
|
| |
cymes
with monochasial branches (branches that only branch on one side, giving
the appearance of one long branch with many flowers on one side): Chelonanthus,
Irlbachia,
Symbolanthus
|
 |
flowers sessile
(flowers without flower stalk, sitting directly on stem):
Tachia,
Tapeinostemon sessiliflorum, many in subtribe Faroinae
|
| |
bracts
and bracteoles scale-like, small (bracts are the small leaves in the
inflorescence, often occur in pairs): most gentians
|
| |
bracts
leaf-like: Macrocarpaea
|
| |
bracts
perfoliate (a pair of bracts that are fused together at their base) : Ixanthus
|
| |
extra
bracts (more than 2) below flower or inflorescence: Fagraea spp.
|
Flowers
(see also Flower anatomy):
| |
3-merous
flowers (3 calyx lobes, 3 corolla lobes, 3 stamens): Pycnosphaera
(rarely in Enicostema)
|
 |
4-merous
flowers:
many gentians, e.g., Canscora, Centaurium
spp., Cicendia, Congolanthus, Coutoubea, Cracosna,
Djaloniella, Exaculum, Faroa, Geniostemon, Hoppea,
Ixanthus [also 5-merous], Karina, Neurotheca, Oreonesion,
Sabatia
spp., Schinziella (rarely in Enicostema)
|
 |
5-merous flowers: most gentians
|
 |
6-merous
corolla:
Chorisepalum, Blackstonia spp.,
Prepusa, Senaea (occasionally
6-7 also in some other genera: Enicostema,
Gentiana,
Irlbachia).
|
 |
8-16-merous
corolla and stamens:
Anthocleista (10-16), Blackstonia (6-12), Potalia (8-10),
Sabatia (4-5,
8-13), Urogentias (8)
|
| |
2
sepals, 4 petals, 4 stamens: Cracosna, Obolaria
|
| |
2
sepal lobes, 5 petals, 5 stamens: Microrphium
|
| |
3
sepals, 4 petals, 4 stamens: Cracosna
|
| |
4
sepals, 6 petals, 6 stamens:
Chorisepalum
|
 |
4
sepals, 8-16 petals, 8-16 stamens: Anthocleista, Potalia
|
 |
hypogynous
(ovary superior):
all gentians
|
 |
unisexual
flowers: Veratrilla and
Gentianella spp.
|
| |
heterostylous
flowers: only in tribe Saccifolieae, e.g.,
Curtia,
Hockinia,
Tapeinostemon spp.,
Voyriella
[Knoblauch, 1895]
|
| |
cleistogamous:
Sebaea oligantha only
|
 |
actinomorphic
(radially symmetric)
flowers: most gentians
|
 |
zygomorphic (bilaterally
symmetric)
flowers: see zygomorphy under calyx, corolla, and stamens below |
 |
erect flowers (upright on the
plant): many gentians |
 |
horizontal flowers (sideways):
many gentians |
 |
nodding flowers (hanging
down): Crawfurdia, Lagenanthus, Lehmanniella,
Lisianthius, Purdieanthus
|
Calyx
(sepals; see also Flower anatomy):
 |
fused
sepals (at least at base of calyx): most gentians
|
| |
free
sepals: Anthocleista,
Chorisepalum, Potalia
|
| |
actinomorphic
(symmetrical) calyx: most gentians
|
| |
zygomorphic
(bilateral) calyx: Exacum spp., Frasera
|
  |
wing
(lower picture)
or keel (upper picture) on back of sepals: Canscora spp., Cicendia, Exacum spp.,
Schultesia
spp., Symbolanthus spp.,
Tachia spp., Tachiadenus spp.
Wings are very thin; keels are thicker at the base.
|
 |
dorsally
thickened sepals: many in tribe Helieae, many also have wings or keels
|
 |
membranaceous
sepals (paper-thin): Prepusa
|
| |
sepals
deciduous (fall off) in fruiting stage:
Chorisepalum,
Macrocarpaea,
Tachia
|
 |
yellow-orange
calyx: Potalia
|
| |
imbricate
calyx lobes in bud: common
|
| |
decussate
calyx lobes in bud: Anthocleista,
Chorisepalum, Potalia
|
| |
membrane
between calyx lobes (intracalycine membrane: Crawfurdia spp.,
Gentiana
spp.
|
Corolla
(petals; see also Flower anatomy):
 |
fused
petals (sympetaly): all gentians are at least fused at the very base of the
petals
|
 |
actinomorphic
corollas (symmetric, all lobes equal): most gentians
|
 |
slightly
zygomorphic corollas (not symmetric, lobes unequal) : e.g., Canscora spp.,
Chelonanthus spp.,
Symbolanthus spp.
|
 |
rotate
corollas (deeply divided, only fused at base, lobes spreading widely): e.g., Frasera,
Swertia
|
 |
tubular
corollas (straight tube, lobes straight): e.g., Potalia spp.
|
 |
salvershaped
corollas (like a trumpet, narrow tube and flaring lobes): e.g., Lisianthius spp.,
Symbolanthus spp.,
Tachia spp.,
Tachiadenus
|
 |
funnelshaped
corollas (like a funnel, narrow tube and lobes spreading, but not flaring): e.g., Chelonanthus, Gentianothamnus, Symbolanthus spp.,
Tetrapollinia
|
 |
bellshaped
corollas (campanulate):
|
 |
tubular corollas that
never open: Gentiana spp. (bottle gentians) are forced open by
bumblebees for pollination, the flowers never open by themselves (see
Pollination) |
 |
contort
corolla lobes in bud (all lobes twisted and overlapping in bud): most gentians
|
| |
imbricate
corolla lobes in bud (lobes overlapping except two, one inner and one
outer): Bartonia, Obolaria,
Saccifolium only
|
| |
valvate+contort
corolla lobes in bud (valvate = lobes not overlapping, only sitting edge
to edge): Aripuana only
|
 |
petal edges erose (papillate):
common in many genera |
 |
petal
edges ciliate or dentate (with hairs or teeth along edge):
Gentianopsis, Pterygocalyx
|
 |
fimbriae
(hairs) at the base of the corolla lobes: Comastoma,
Gentiana,
Gentianella
spp.
|

 |
folds (plicae)
between corolla lobes (thinner folded tissue fusing corolla lobes):
Crawfurdia,
Gentiana spp., Metagentiana,
Tripterospermum
|
 |
each
petal with a spur (a thin, long and hollow structure attached to a petal):
Halenia only
|
 |
white
petals: e.g., Anthocleista, Coutoubea,
Enicostema,
Irlbachia spp.,
Fagraea
spp.,
Saccifolium, Symbolanthus spp., Tachiadenus spp.
|
 |
yellow
petals: e.g., Blackstonia spp., Ixanthus spp., Sebaea spp.,
|
 |
orange
petals: e.g., Lagenanthus spp., Tapeinostemon spp.,
|
 |
red
petals: e.g., Gentianella spp., Rogersonanthus spp.,
Symbolanthus spp.
|
 |
pink
petals: e.g., Centaurium spp., Sabatia,
Symbolanthus spp.
|
 |
purple
petals: e.g., Anthocleista spp.,
Chelonanthus spp., Exacum spp.,
Gentianella spp., Halenia
spp.
|
 |
blue
petals: e.g., Exacum spp., Gentiana spp.
|
| |
black
petals: Lisianthius nigrescens
|
 |
green
petals: e.g., Chelonanthus spp.,
Macrocarpaea spp., Potalia spp.
|
 |
petals
with nectar guides (stripes inside corolla mouth and/or on lobes):
Symbolanthus spp.
|
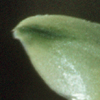 |
Corolla with darker lobe
apices: some Helieae |
| |
corolla
with lighter-colored 'eye' in middle of flower: Eustoma, Sabatia
|
| |
corolla
persistent in fruit (does not fall off when fruits develop): many
Gentianeae and Chironieae
|
Glands
in the flower (see also Flower anatomy):
| |
colleters
(small, finger-shaped glands on inside of sepals): common in many gentians
and other families of the Gentianales
|
| |
colleters
absent from calyx: e.g., Bisgoeppertia,
Coutoubea, Cracosna,
Eustoma
|
| |
glandular
ridge on back of sepals: common in Helieae
|
 |
nectaries
on
inside of corolla tube or on lobes: Frasera spp.,
Gentianella spp.,
Swertia
spp.,
|
| |
nectary
disk at base of ovary: many in tribes Potalieae and
Helieae, a few in subtribe Gentianinae, e.g., Gentianothamnus, Tripterospermum
|
| |
glands
at apex of anther: Sebaea spp.
|
| |
glands
at base of anther: Sebaea spp.
|
Stamens
(androecium, filaments, anthers; see also Flower
anatomy):
| |
stamens
fewer than corolla lobes: Canscora spp., Hoppea, Schinziella
|
| |
stamens
alternating with corolla lobes: all gentians
|
 |
stamens inserted in the corolla tube: most gentians
|
| |
stamens
inserted in the corolla lobe sinuses: e.g.,
Aripuana, Djaloniella,
Faroa, Geniostemon, Sabatia,
Swertia spp.
|
| |
actinomorphic
stamens (symmetric): most gentians
|
 |
zygomorphic
stamens (assymmetric) : e.g.,
Calolisianthus,
Chelonanthus, Cotylanthera,
Exacum spp., Orphium, and
Symbolanthus
|
| |
anisomorphic
stamens (stamens of different shapes and sizes): Canscora, Hoppea, Schinziella
|
| |
corona
at the base of stamens (ring of tissue): Symbolanthus only
|
| |
appendages
at base of stamens (flaps, hoods, wings): common in subtribe Faroinae and
Coutoubea
|
| |
flattened
filaments: many in tribe Saccifolieae
|
| |
curved
filaments:
Gentiana
sect. Stenogyne and Tripterospermum
|
| |
winged
filaments: Gentiana spp.
|
| |
apically
recurved filaments (filament strongly turned close to the anther): many in tribe Helieae
|
| |
fused
(partially or completely) filaments: Anthocleista, Potalia
|
| |
fused
(connate) anthers: Gentiana spp., Sebaea spp., Tachiadenus spp. [Duncan
& Brown, 1954]
|
| |
long,
linear anthers: e.g., Anthocleista, Deianira, Fagraea spp.,
Potalia, and many in tribe Helieae
|
 |
recurved
(bent)
anthers: many in tribe Helieae, e.g., Chelonanthus, Symbolanthus
|
 |
spirally
twisted/coiled anthers: many in subtribe Chironiinae, e.g., Centaurium,
Chironia, Orphium, Sabatia, Canscora
|
| |
twisted
backwards anthers: Sebaea spp.
|
| |
longitudinally
dehiscent anthers (with slits): most gentians
|
 |
sagittate anthers (V-shaped,
split at base): many gentians [photo shows anther upside down] |
| |
poricidal
anthers (pores at apex): Cotylanthera (1 pore), Exacum spp. (2 pores)
|
| |
introrse
anthers (open toward the middle of flower, on the inside of the anther): most gentians
|
| |
latrorse
anthers (open toward the sides of the anthers): Voyriella spp.,
Saccifolium
|
| |
anthers
with apical appendages (with extra tissue on the tip of the anther): many in tribes Exaceae,
Helieae, and Saccifolieae
|
| |
anthers
with basal appendages: some in tribe Exaceae
|
| |
coriaceous
anthers (leathery, thick anthers): Exacum, Gentianothamnus
|
Gynoecium
(pistil, ovary, style, stigma; see also Flower anatomy
and Fruits, below) [Gopal Krishna & Puri, 1962]:
| |
bicarpellate
gynoecium (formed from 2 fused carpels): all gentians
|
| |
syncarpous
gynoecium: all gentians
|
| |
stipitate
gynoecium (on gynophore): many in tribe Gentianeae
|
| |
sessile
gynoecium: most gentians
|
 |
style
long, filiform, distinct: many in tribes Exaceae,
Helieae, Potalieae
|
| |
style
twisted when dry: many Helieae
|

 |
style
zygomorphic: many in tribe Exaceae and
Helieae
|
| |
style
short or absent: many in tribe Gentianeae
|
| |
decurrent
stigma along carpel sutures: Bartonia, Lomatogonium spp.
|
| |
with
additional lower stigma: Sebaea spp. [Marloth, 1909]
|
 |
strongly
bilamellate (bilobed) stigma: many Helieae, Fagraea spp., Centaurium,
Eustoma
|
 |
capitate
stigma: common, e.g., Lisianthius, Potalia
|
| |
simple
stigma: common in tribe Exaceae
|
| |
peltate
stigma: Voyria spp.
|
 |
long,
coiling stigmatic lobes: Sabatia
|
Fruits
(see also Flower anatomy and Gynoecium, above):
 |
capsules,
dry and thin:
most gentians
|
| |
capsules,
leathery: Symbolanthus
|
| |
capsules,
woody: Chorisepalum,
Tachia
|
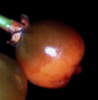 |
berries:
Anthocleista, Chironia baccifera, Fagraea, Potalia,
Tripterospermum spp.
(many different colors)
|
| |
apical,
septicidal dehiscence (opens from top along sutures): most gentians with capsules
|
| |
apical
dehiscence, with coriaceous lid: Exacum spp.
|
 |
medial
dehiscence (opens in the middle): some Helieae, Voyria spp.
|
| |
capsule
splits into 4 valves: Macrocarpaea spp.,
Chorisepalum
|
| |
indehiscent
fruits (never opens): Symbolanthus spp.?, Voyria spp.?, and the genera with berries
|
| |
parietal
placentation (placenta attached to fruit wall): many gentians (this character is very plastic and both
parietal and axile placentation can be found within the same
gynoecium/fruit in some species)
|
| |
axile
placentation (placenta attached to fruit center), at least for 1/2 of the length of the fruit: many in tribe Exaceae, some in Helieae
|
| |
intruding
placentas (placenta large and intruding far into the fruit from the walls
and/or center): common in many gentians, especially in tribe Helieae, e.g.,
Anthocleista, Centaurium, Fagraea, Gentianothamnus,
Tachiadenus
|
| |
seeds
distributed over entire inner wall of fruit: many in subtribe Swertiinae
|
Seeds
(see also Embryology; [Bouman et al., 2002;
Grothe & Maas, 1984]):
| |
numerous
seeds: most gentians
|
| |
round
or oblong seeds: Tachia spp., Tachiadenus spp., Voyria spp.
|
| |
flattened
seeds: many in tribe Gentianeae, in subtribe Potaliinae,
Chorisepalum,
Macrocarpaea spp.
|
| |
cup-shaped
seeds: Exacum spp., Voyria spp.
|
| |
winged
seeds: some in tribe Gentianeae, Chorisepalum,
Macrocarpaea spp.
|
| |
angular
seeds: common in tribes Exaceae and
Helieae
|
| |
filiform
seeds: Voyria spp.
|
| |
dust
seeds (very small): Voyria
|
| |
aril:
absent in all gentians
|
| |
aborted
seeds, filiform: Voyria spp.
|
spp.
= some species, this indicates that some but not all investigated species
in the genus has this character
e.g.=
for example

|
|
























































